In the grand blueprint of modern construction, the excavator stands as an indispensable “iron giant,” leveraging its formidable digging prowess and flexibility to play a pivotal role across various sectors such as civil engineering, mining, road construction, and water conservancy facilities. The efficient operation of an excavator hinges on the synergistic efforts of its intricately designed components. Below, we delve into several key parts of an excavator and their respective functions.
Power System
At the heart of an excavator lies its powerful diesel engine, serving as the primary source of energy. This engine converts the combustion of diesel fuel into mechanical energy, driving the entire machine. The performance of the engine directly impacts the excavator’s digging force, mobility, and operational efficiency. To cater to diverse working conditions, modern excavator engines often employ advanced fuel injection technology, turbocharging systems, and intelligent control systems for more efficient and environmentally friendly operation.
parts of a excavator

Hydraulic System
The hydraulic system acts as the lifeblood of an excavator, responsible for transmitting the power generated by the engine to various working devices. Comprising hydraulic pumps, cylinders, motors, and control valves, this system harnesses the power of pressurized hydraulic fluid to facilitate the excavator’s digging, slewing, and traveling movements. The advantage of a hydraulic system lies in its ability to transmit substantial forces smoothly and facilitate automated control. Thus, every intricate movement of the excavator is intricately orchestrated by the precision control of its hydraulic system.
Working Devices
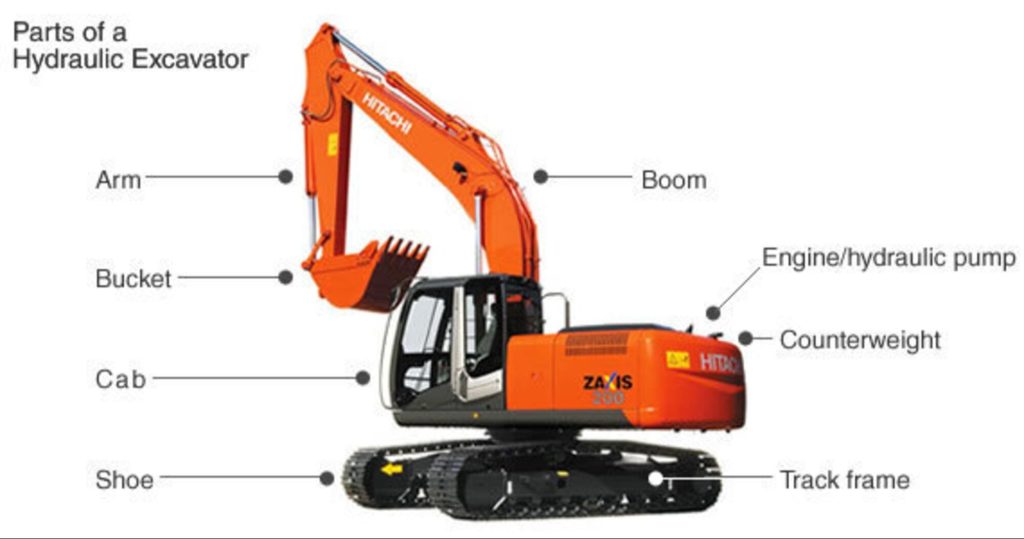
The working devices are the direct implements of the excavator’s digging operations, encompassing the boom, arm, bucket, and accompanying hydraulic cylinders and connectors. The boom supports and moves the entire working assembly, while the arm adjusts the position and angle of the bucket. The bucket, in turn, serves as the tool for actual material excavation. Through the action of the hydraulic system, these components flexibly combine to execute complex actions such as digging, loading, and unloading.
Slewing Platform
Positioned at the center of the excavator’s body, the slewing platform acts as a pivotal link between the upper working devices and the lower tracking devices. It not only bears the weight of the entire working assembly but also allows the working devices to rotate 360 degrees within the horizontal plane, vastly expanding the excavator’s operational range. The slewing platform typically incorporates a slewing motor and control valves to ensure smooth and precise rotational movements.
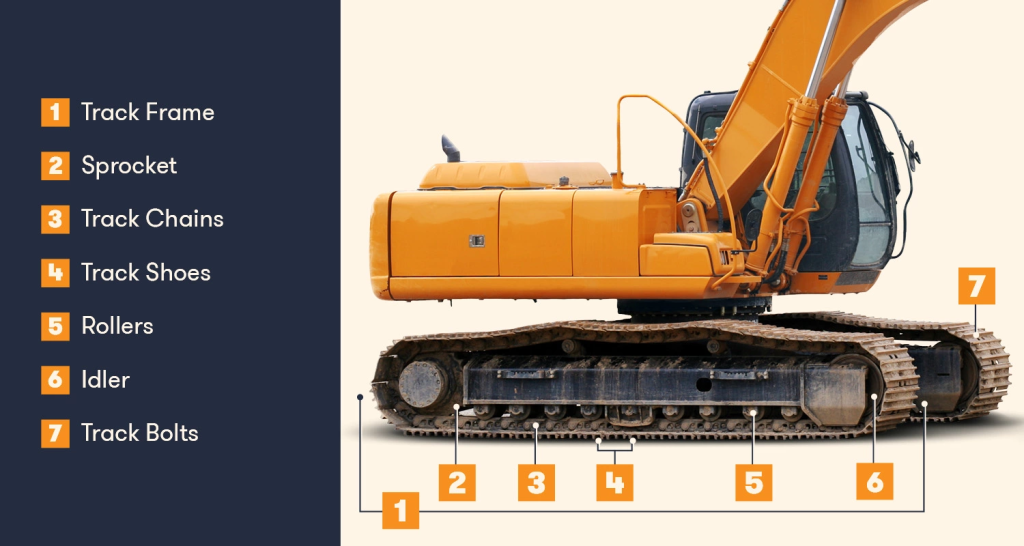
Tracking Devices
The tracking devices of an excavator can be categorized into crawler-type and wheel-type, depending on the model and intended use. Crawler-type excavators feature wide tracks that provide exceptional off-road performance and stability, ideal for challenging terrains. In contrast, wheel-type excavators facilitate rapid mobility on flat surfaces, making them more suitable for short-distance transfers and urban operations. The design of the tracking devices meticulously balances the excavator’s stability and maneuverability, ensuring stable operation across various working conditions.
Conclusion
As a vital tool in modern engineering construction, the excavator’s high efficiency, flexibility, and robust performance are underpinned by the synergistic efforts of its intricate components. From the powerful engine that fuels its operations to the precise hydraulic system that orchestrates its movements, from the versatile working devices that execute digging tasks to the stable tracking devices that ensure mobility, every component embodies the ingenuity and technological prowess of engineers. With continuous technological advancements and innovations, the excavator’s performance will continue to soar, contributing even more significantly to humanity’s modernization endeavors.