excavator body parts name|excavator components diagram|what are the parts of an excavator called
Excavators are powerful machines used in construction, mining, and other industries for digging, lifting, and moving materials. Understanding the various body parts of an excavator is essential for operators, technicians, and enthusiasts to comprehend how these machines operate efficiently. Let’s delve into the key body parts of an excavator:
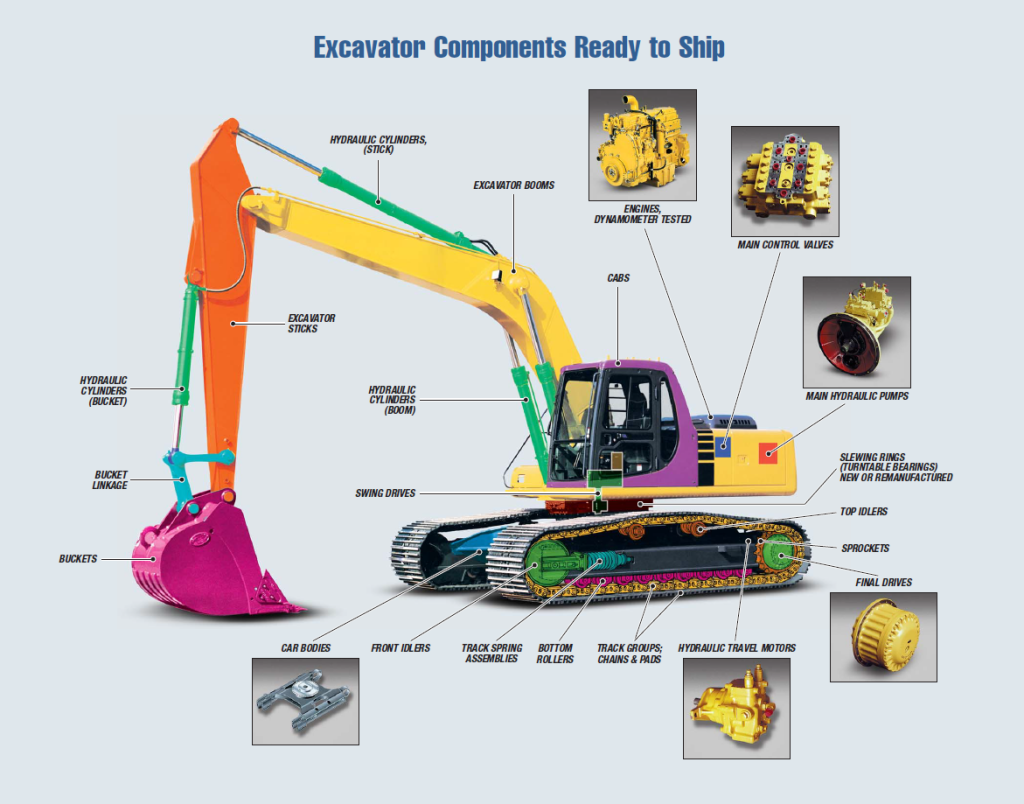
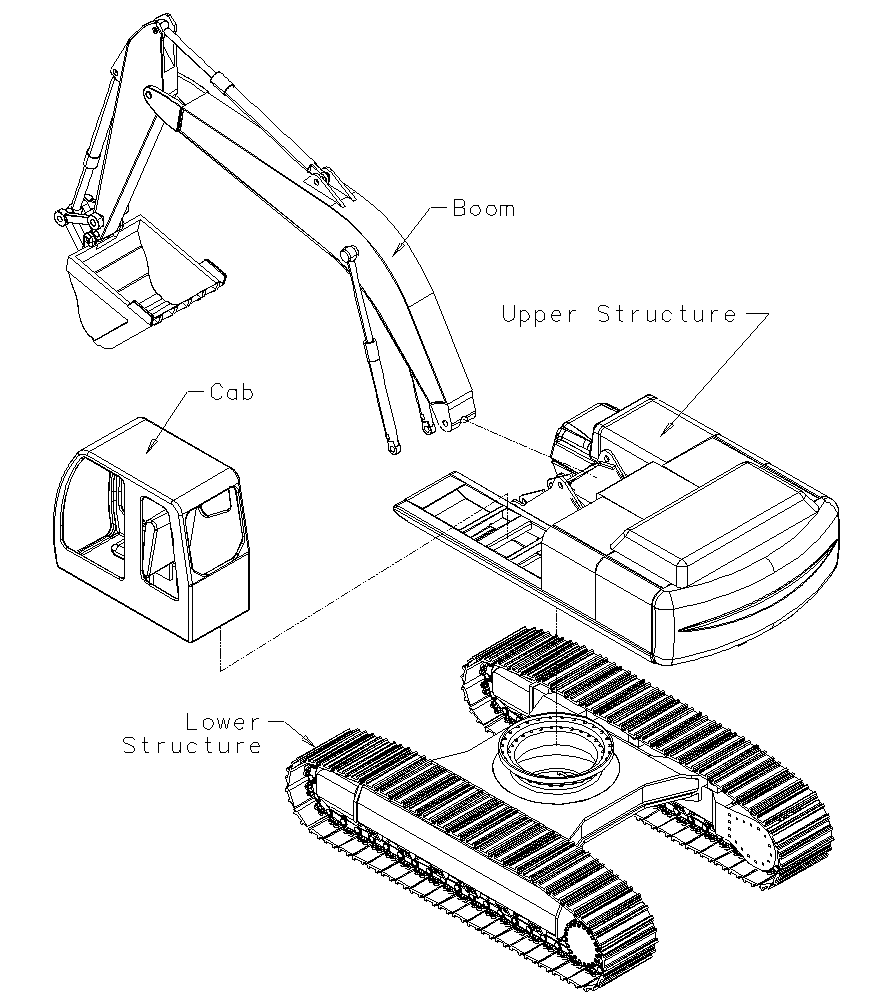
- Cabin:
The cabin, also known as the operator cab, is where the operator controls the excavator. It is equipped with a comfortable seat, controls (joysticks, pedals, levers), instrumentation panel, and windows for visibility. The cabin provides a safe and ergonomic environment for the operator to oversee operations. - Engine Compartment:
The engine compartment houses the excavator’s power source, typically a diesel engine. It contains components such as the engine, fuel tank, air filter, cooling system, and exhaust system. The engine provides the necessary power to drive the hydraulic system and move the excavator. - Counterweight:
The counterweight is located at the rear of the excavator’s upper structure. It balances the weight of the boom, arm, and attachments when lifting heavy loads. The counterweight enhances the stability of the machine and prevents tipping during operation. - Swing Platform:
The swing platform is the rotating base of the excavator where the upper structure sits. It allows the upper structure to rotate 360 degrees, enabling the excavator to reach various areas without repositioning the entire machine. The swing platform is supported by the undercarriage. - Undercarriage:
The undercarriage consists of tracks or wheels, rollers, idlers, and sprockets. It provides stability and mobility to the excavator, allowing it to move across different terrains and support the weight of the upper structure. The undercarriage is essential for the excavator’s maneuverability. - Boom:
The boom is the long, vertical arm of the excavator that extends from the machine’s body. It provides reach and height for digging, lifting, and reaching over obstacles. The boom is connected to the machine via hydraulic cylinders for movement. - Arm:
The arm, also known as the dipper or stick, is attached to the end of the boom. It works in conjunction with the boom to provide horizontal movement and precision control when excavating or reaching into specific areas. - Bucket:
The bucket is the attachment at the end of the arm that scoops, lifts, and dumps materials. Buckets come in various sizes and configurations to suit different excavation needs, such as digging, trenching, or loading.
Understanding the body parts of an excavator and their functions is crucial for operating the machine effectively and maintaining its performance. Proper maintenance, regular inspections, and adherence to safety protocols are essential for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of excavators in demanding work environments. Each body part plays a vital role in the overall functionality of the excavator, making it a versatile and indispensable piece of equipment in various industries.